The Project
Ocean acidification is linked to the oceanic absorption of approximately 30% of
anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
The future evolution of ocean acidification
depends on the trajectory of atmospheric CO2 over the coming decades
and associated climate change.
In this data visualization project historical and future projections of ocean
acidification markers from Earth System Model
experiments are displayed.
Explore the Data
Historical and future model projections performed by the CMIP5 models can be explored in an intuitive
fashion across a variety of interactive visualizations,
including spatial and temporal distribution, carbon budgets
and relative changes in global and regional scales.
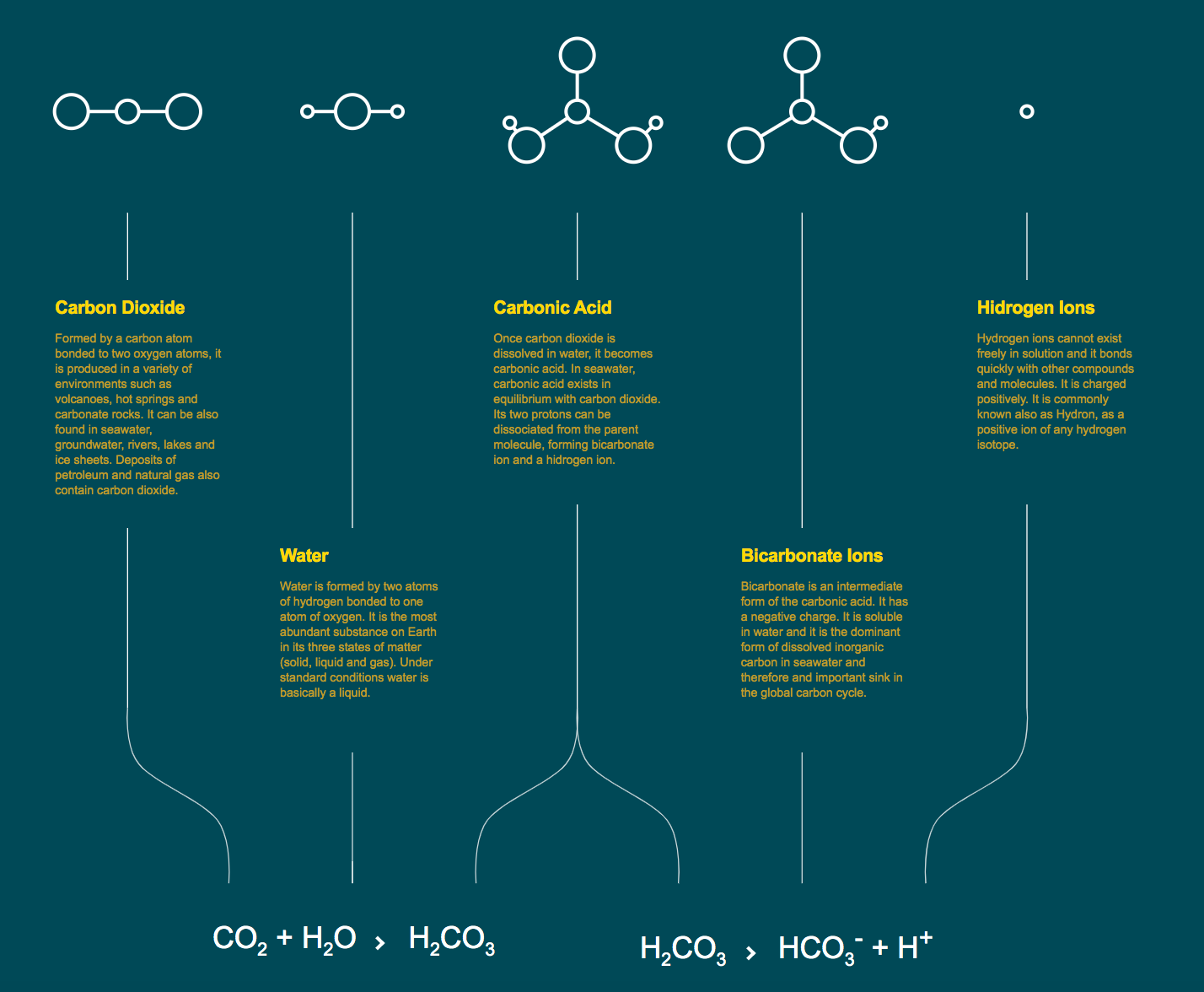
Carbonate Chemistry
Different carbonate chemistry species are involved in the reactions that result in the reduction of
seawater pH. These reactions are explained here, along with the relative proportion of these species
and the contribution of aerosols and rivers to coastal acidification.
Earth System Models
Model projections are performed using Earth System Models, complex numerical architectures that allow
the present and future projection of climate variables on a global scale.
These numerical tools are explained in this section along with the context in which
they are used and relevant UN IPCC standards.